
Martin MBBS, FRACP, in Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine, 2020 Apgar Score However, when a child has cerebral palsy, low Apgar scores alone are not adequate evidence that perinatal hypoxia was responsible for the neurologic injury. 51,52 The Apgar score is more likely to predict a poor neurologic outcome when the score remains 3 or less at 10, 15, and 20 minutes. 50Īdditional studies have suggested that Apgar scores are poor predictors of long-term neurologic impairment. 50 The biophysical profile includes performance of a nonstress test and ultrasonographic assessment of fetal tone, fetal movement, fetal breathing movements, and amniotic fluid volume. 43-49 By contrast, the fetal biophysical profile has a good correlation with the acid-base status of the fetus and the neonate (see Chapter 6). Other studies, including those of low-birth-weight infants, have found that a low Apgar score is a poor predictor of neonatal acidosis, although a high score is reasonably specific for excluding the presence of severe acidosis. 42 noted a poor correlation between the Apgar score and the umbilical cord blood pH. In a prospective study of 1210 deliveries, Sykes et al.
Several studies have challenged the notion that a low Apgar score signals perinatal asphyxia. 41 In addition, the one-minute Apgar score was a better predictor of mortality within the first 2 days of life than within 2 to 28 days of life. She noted that the risk for neonatal mortality was inversely proportional to the 1-minute score. Apgar cautioned against the use of the Apgar score to make these predictions in an individual infant.

The scoring system may help predict mortality and neurologic morbidity in populations of infants, but Dr. The Apgar score is widely used to assess neonates, although its value has been questioned.
#Apgar score serial
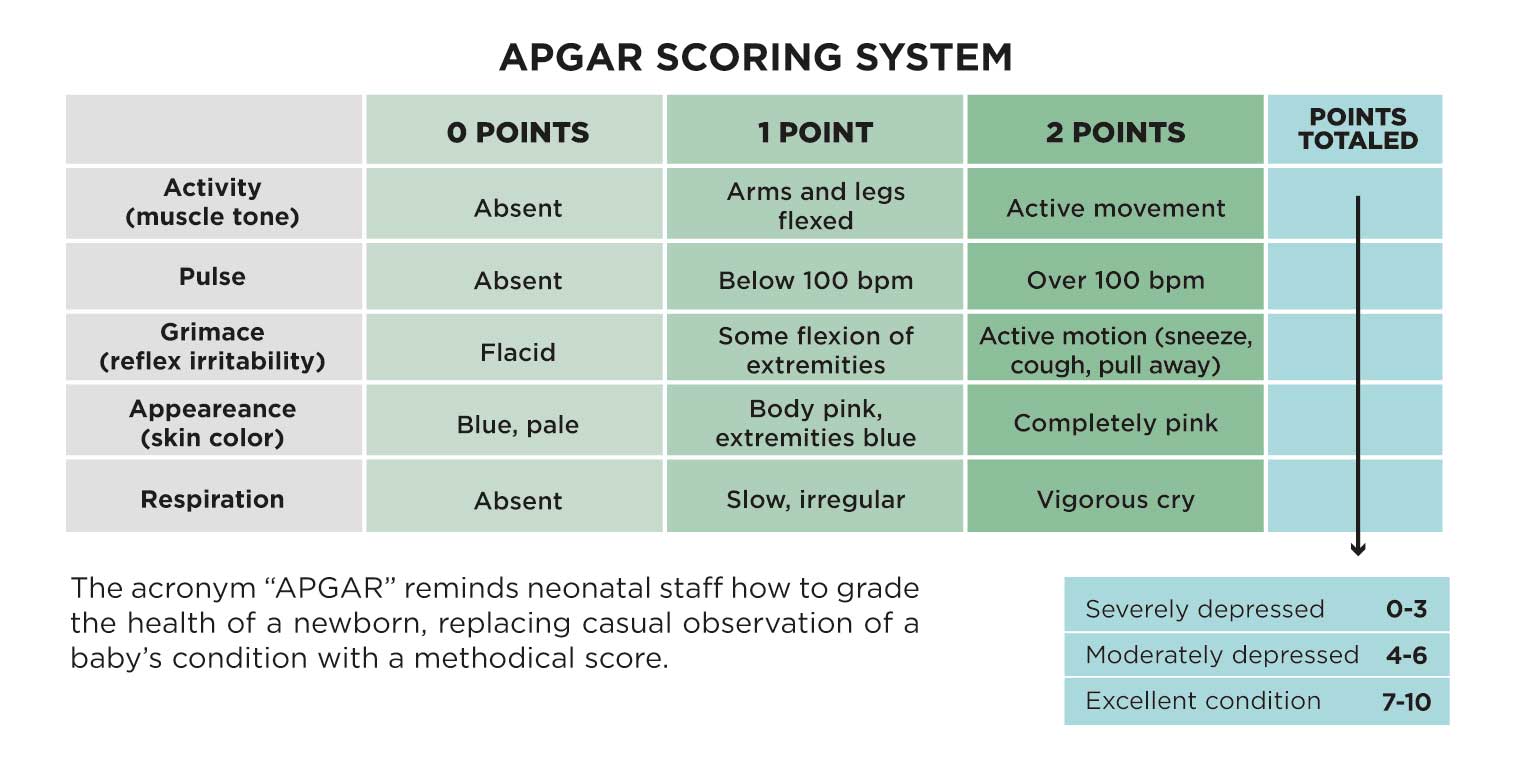
Apgar emphasized that this system does not replace a complete physical examination and serial observations of the neonate for several hours after birth. A total score of 8 to 10 is normal, a score of 4 to 7 indicates moderate impairment, and a score of 0 to 3 signals the need for immediate resuscitation. A score of 0, 1, or 2 is assigned for each of these five entities ( Table 9.1). The parameters are: heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex irritability, and color. Further scoring at 5- or 10-minute intervals may be done if initial scores are low. The Apgar score is based on five parameters that are assessed at 1 and 5 minutes after birth. 39 She suggested that this standardized and relatively objective scoring system would differentiate between infants who require resuscitation and those who need only routine care. In 1953, Virginia Apgar, an anesthesiologist, described a simple method for neonatal assessment that could be performed while care is being delivered. Because NRP instructions require simultaneous assessment and treatment, it is important that the neonatal assessment be both simple and sensitive. Resuscitative efforts typically precede the performance of a thorough physical examination of the neonate. Chestnut MD, in Chestnut's Obstetric Anesthesia, 2020 Apgar Score


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
